lv size echo | lv cavity size lv size echo tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations. GUIDE TO CHEROKEE SYLLABARY PRONUNCIATION. GUIDE TO CHEROKEE SYLLABARY PRONUNCIATION: (PHONIC) PRONUNCIATION:(THE ALPHABET READS STRAIGHT ACROSS, LEFT TO RIGHT. FROM ROW TO ROW . THERE ARE (13) ROWS TOTAL) Row Number One: "a" is said as ah. "e" is said as .
0 · normal lv size
1 · normal lv end diastolic diameter
2 · normal lv dimensions
3 · normal lv diameter
4 · lv cavity size
5 · left internal dimension in systole
6 · echocardiography normal values pdf
7 · 2d lv pw abnormal
Steve Marcus. The Chicken Ranch, a licensed, legal brothel near Pahrump, is pictured Thursday, May 6, 2021. Nevada’s legal brothels were given the green light to reopen May 1 after being closed.
tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations. Each echocardiogram includes an evaluation of the LV dimensions, wall thicknesses and function. Good measurements are essential and may have implications for .Normal Ranges for LV Size and Function Normal values for LV chamber dimensions (linear), volumes and ejection fraction vary by gender. A normal ejection fraction is 53-73% (52-72% for men, 54-74% for women).tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations.
Each echocardiogram includes an evaluation of the LV dimensions, wall thicknesses and function. Good measurements are essential and may have implications for therapy. The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view.Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each . ∗ LV size applied only to chronic lesions. Normal 2D measurements: LV minor axis ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2 , LV end-diastolic volume ≤ 82 ml/m 2 , maximal LA antero-posterior diameter ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2 , maximal LA volume ≤ 36 ml/m 2 (2;33;35). The first and most commonly used echocardiography method of LVM estimation is the linear method, which uses end-diastolic linear measurements of the interventricular septum (IVSd), LV inferolateral wall thickness, and LV internal diameter derived from 2D-guided M-mode or direct 2D echocardiography.

Summary. Reference ranges for left ventricular volumes and ejection fraction as well as LA volumes have changed in the recent guidelines due to the use of large echo databases. Left ventricular wall motion scoring has changed to a 4-grade system. This study demonstrates a marked discrepancy in recommended measures of LV size obtained by echocardiography in a large cohort of patients receiving contrast for clinical purposes. They evaluated the reproducibility of LV dimension, area, volumes, and indices of systolic function by 2D echocardiography in a cohort of 169 children (mean age, 9.5 years; range, 0.2–20.6 years) with dilated cardiomyopathy. Estimation of left ventricular (LV) size and function remains one of the most frequent indications for echocardiography. In the majority of cases, LV function is estimated qualitatively using the eyeball method or quantitatively using the two-dimensional (2D) biplane Simpson method of disks.
Normal Ranges for LV Size and Function Normal values for LV chamber dimensions (linear), volumes and ejection fraction vary by gender. A normal ejection fraction is 53-73% (52-72% for men, 54-74% for women).tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations.
Each echocardiogram includes an evaluation of the LV dimensions, wall thicknesses and function. Good measurements are essential and may have implications for therapy. The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view.Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each . ∗ LV size applied only to chronic lesions. Normal 2D measurements: LV minor axis ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2 , LV end-diastolic volume ≤ 82 ml/m 2 , maximal LA antero-posterior diameter ≤ 2.8 cm/m 2 , maximal LA volume ≤ 36 ml/m 2 (2;33;35). The first and most commonly used echocardiography method of LVM estimation is the linear method, which uses end-diastolic linear measurements of the interventricular septum (IVSd), LV inferolateral wall thickness, and LV internal diameter derived from 2D-guided M-mode or direct 2D echocardiography.
Summary. Reference ranges for left ventricular volumes and ejection fraction as well as LA volumes have changed in the recent guidelines due to the use of large echo databases. Left ventricular wall motion scoring has changed to a 4-grade system. This study demonstrates a marked discrepancy in recommended measures of LV size obtained by echocardiography in a large cohort of patients receiving contrast for clinical purposes. They evaluated the reproducibility of LV dimension, area, volumes, and indices of systolic function by 2D echocardiography in a cohort of 169 children (mean age, 9.5 years; range, 0.2–20.6 years) with dilated cardiomyopathy.
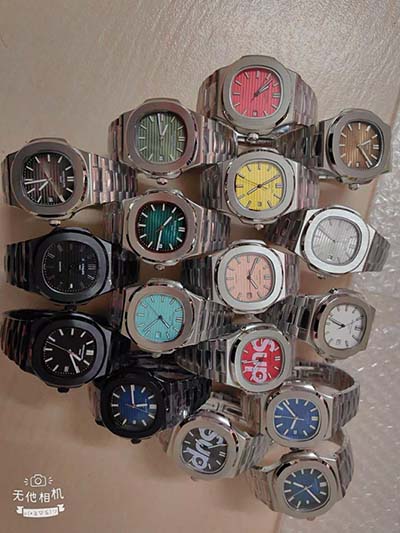
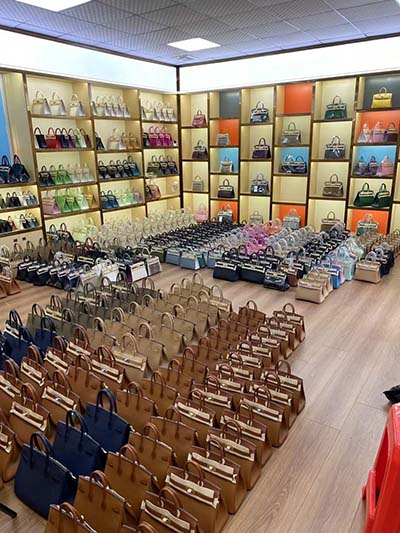
celebrity wear lv bag
normal lv size
normal lv end diastolic diameter
normal lv dimensions

Home
lv size echo|lv cavity size